|
Home >> Tutorials/FAQs >> CSS Tutorials >> Index
CSS Tutorials - Understanding Multiple Element Formatting Rules
By: FYICenter.com
Part:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(Continued from previous part...)
How Is the Width a Parent Element Related to Child Elements?
If child block elements are enclosed in a parent block element, the width of the parent element is
related to child block elements based on the following rules:
- The full width of a block element is the sum of left margin, left border, left padding, width,
right padding, right border, and right margin.
- The full width of a stack of block elements is the maximum value of full widths of block elements
in the stack.
- The final width of the parent element equals to the final full width of the stack of the all child elements.
- If the width of the parent element is not specified, the final width of the parent element will be
set to the full width of the child stack.
- If the width of the parent element is specified and greater than the full width of the child stack.
the full width of the child stack will be extended match the specified width of the parent element.
- If the width of the parent element is specified and less than the full width of the child stack.
the width of the parent element will be extended match the full width of the child stack.
How Is the Full Width of a Block Element Extended?
If the full width of a block element needs to be extended to meet the width of the parent element,
brower will following there rules:
The full width of a block element is the sum of left margin, left border, left padding, width,
right padding, right border, and right margin.
There are only 3 out of the 7 horizontal spacing properties can to assigned with the value of "auto":
left margin, width, and right margin.
If none of the 7 horizontal spacing properties is assigned to "auto", right margin will be extended
to meet the full width extension requirement.
If right margin is assigned to "auto", it will be extended to meet the full width extension requirement.
If right margin is not assigned to "auto", and one or more other properties are assigned to "auto", other
properties will be extended to meet the full width extension requirement.
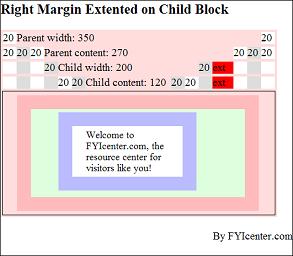
How To Test Child Full Width Extension?
One of the horizontal formatting rules says: if the width of the parent element is specified and greater than the full width of the child stack.
the full width of the child stack will be extended match the specified width of the parent element.
The HTML and CSS document shows you a good example on this rule:
<html><head>
<style type="text/css">
H1 {font-size: 20px}
DIV.page {width: 425px; border: 1px solid black}
TABLE#out {background-color: #ffdddd}
TD#box {border: 1px solid black}
DIV#parent {width: 350px;
margin: 5px 20px 5px 20px;
border: 20px solid #ffbbbb;
padding: 5px 20px 5px 20px;
background-color: #ddffdd}
P#child {width: 200px;
margin: 5px 20px 5px 20px;
border: 20px solid #bbbbff;
padding: 5px 20px 5px 20px;
font-size: 14px;
background-color: #ffffff}
SPAN#parentWidth {width: 350px}
SPAN#parentContent {width: 270px}
SPAN#childWidth {width: 200px}
SPAN#child {width: 120px}
SPAN#w20 {width: 20px; background-color: #ffffff}
SPAN#g20 {width: 20px; background-color: #dddddd}
SPAN#ext {width: 30px; background-color: #ff0000}
</style>
</head><body><div class="page">
<H1>Right Margin Extented on Child Block</H1>
<table id=out><tr><td>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
<span id=parentWidth>Parent width: 350</span>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
</td></tr><tr><td>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
<span id=g20>20 </span>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
<span id=parentContent>Parent content: 270</span>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
<span id=g20>20 </span>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
</td></tr><tr><td>
<span id=w20> </span>
<span id=g20> </span>
<span id=w20> </span>
<span id=g20>20 </span>
<span id=childWidth>Child width: 200</span>
<span id=g20>20 </span>
<span id=ext>ext </span>
<span id=w20> </span>
<span id=g20> </span>
<span id=w20> </span>
</td></tr><tr><td>
<span id=w20> </span>
<span id=g20> </span>
<span id=w20> </span>
<span id=g20> </span>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
<span id=g20>20 </span>
<span id=child>Child content: 120</span>
<span id=g20>20 </span>
<span id=w20>20 </span>
<span id=g20> </span>
<span id=ext>ext </span>
<span id=w20> </span>
<span id=g20> </span>
<span id=w20> </span>
</td></tr><tr>
<td id=box><div id=parent><p id=child>
Welcome to FYIcenter.com, the resource
center for visitors like you!
</p></div></td>
</tr></table>
<p align="right">By FYIcenter.com</p>
<div></body></html>
Save this document as ChildBlockExtension.html, and view it with a browser,
you will see how the right margin of the child block is extended to meet the specified width of the parent block:
(Continued on next part...)
Part:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|