Iterator Event Types
I
TERATOR
API
83
ing iterator events is
XMLEventReader
, and the primary interface for writing iter-
ator events is
XMLEventWriter
. The
XMLEventReader
interface contains five
methods, the most important of which is
nextEvent()
, which returns the next
event in an XML stream.
XMLEventReader
implements
java.util.Iterator
,
which means that returns from
XMLEventReader
can be cached or passed into
routines that can work with the standard Java Iterator; for example:
public interface XMLEventReader extends Iterator {
public XMLEvent nextEvent() throws XMLStreamException;
public boolean hasNext();
public XMLEvent peek() throws XMLStreamException;
...
}
Similarly, on the output side of the iterator API, you have:
public interface XMLEventWriter {
public void flush() throws XMLStreamException;
public void close() throws XMLStreamException;
public void add(XMLEvent e) throws XMLStreamException;
public void add(Attribute attribute) \
throws XMLStreamException;
...
}
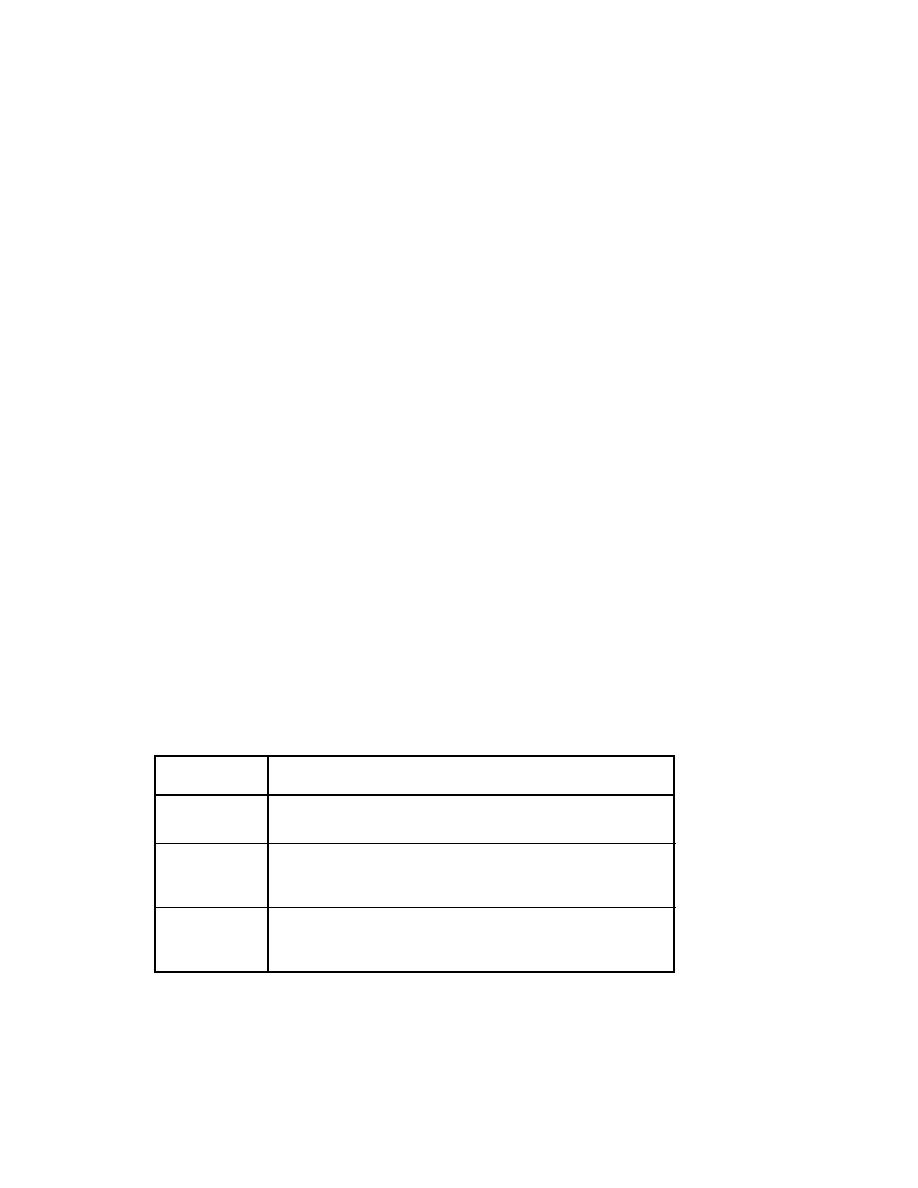
Iterator Event Types
XMLEvent
types defined in the event iterator API.
Table 42
XMLEvent
Types
Event Type
Description
StartDocu-
ment
Reports the beginning of a set of XML events, including encoding,
XML version, and standalone properties.
StartEle-
ment
Reports the start of an element, including any attributes and namespace
declarations; also provides access to the prefix, namespace URI, and
local name of the start tag.
EndElement
Reports the end tag of an element. Namespaces that have gone out of
scope can be recalled here if they have been explicitly set on their corre-
sponding
StartElement.
