Overviewof Web Application Security
Overviewof Web Application Security
server. Web components are either Java servlets, JSP pages, JSF pages, or web service endpoints.
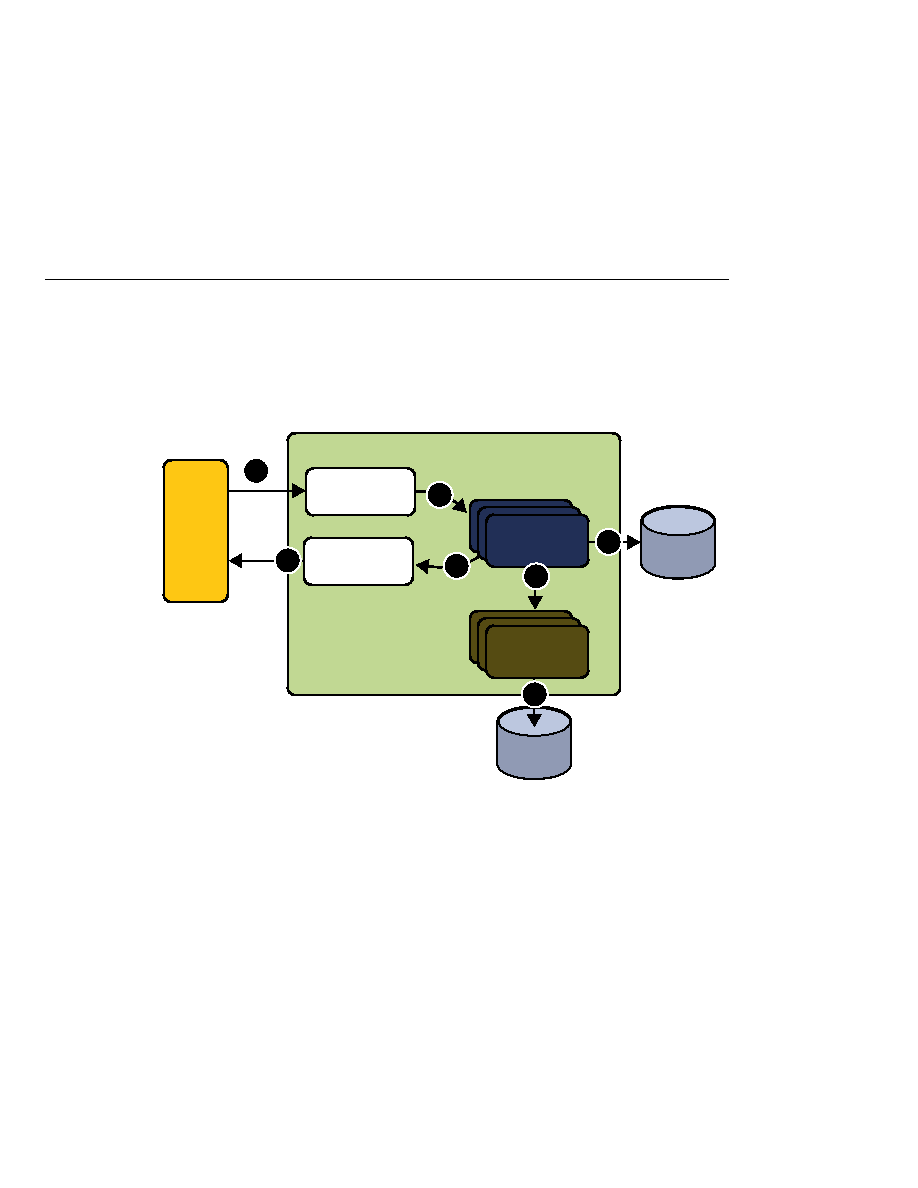
The interaction between a web client and a web application is illustrated in
web container provides services such as request dispatching, security, concurrency, and
life-cycle management.
or deployed, to the web container. Annotations and/or deployment descriptors are used to relay
information to the deployer about security and other aspects of the application. Specifying this
information in annotations or in the deployment descriptor helps the deployer set up the
appropriate security policy for the web application. Any values explicitly specified in the
deployment descriptor override any values specified in annotations. This chapter provides
more information on configuring security for web applications.
using the HTTPS protocol, read