Web Application Life Cycle
Web Application Life Cycle
Web Application Life Cycle
A web application consists of web components, static resource files such as images, and helper
classes and libraries. The web container provides many supporting services that enhance the
capabilities of web components and make them easier to develop. However, because a web
application must take these services into account, the process for creating and running a web
application is different from that of traditional stand-alone Java classes.
The process for creating, deploying, and executing a web application can be summarized as
follows:
1. Develop the web component code.
2. Develop the web application deployment descriptor.
3. Compile the web application components and helper classes referenced by the components.
4. Optionally package the application into a deployable unit.
5. Deploy the application into a web container.
6. Access a URL that references the web application.
Developing web component code is covered in the later chapters. Steps 2 through 4 are
expanded on in the following sections and illustrated with a Hello, World-style
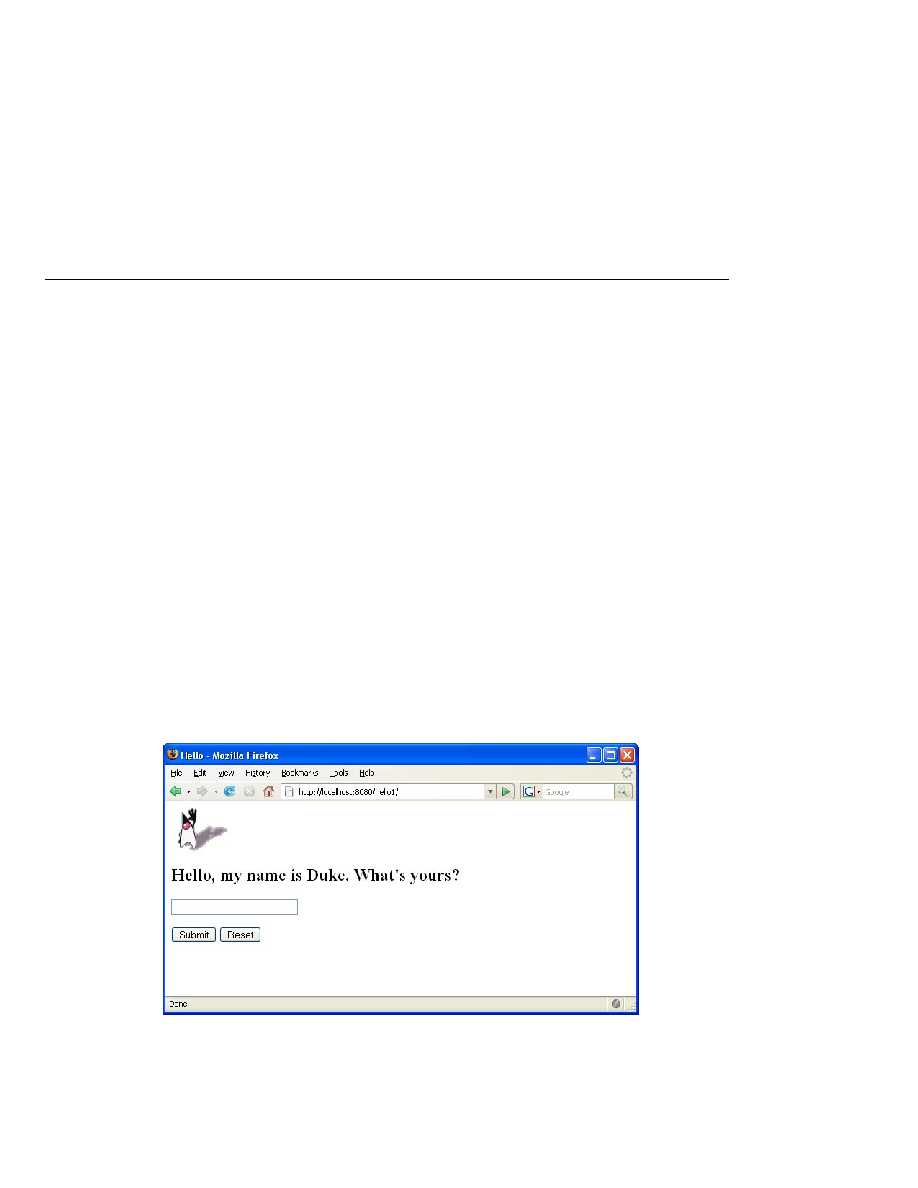
presentation-oriented application. This application allows a user to enter a name into an HTML
form (
) and then displays a greeting after the name is submitted (
FIGURE 33
Greeting Form
Web Application Life Cycle
The Java EE 5 Tutorial · September 2007
80
