|
Network layer firewalls
Java Security,Windows code security, Windows Server 2003 Security,Internet Explorer 7 Security and Internet Firewalls questions and answers
(Continued from previous question...)
Network layer firewalls
These generally make their decisions based on the source, destination addresses and ports (see Appendix 6 for a more detailed discussion of ports) in individual IP packets. A simple router is the ``traditional'' network layer firewall, since it is not able to make particularly sophisticated decisions about what a packet is actually talking to or where it actually came from. Modern network layer firewalls have become increasingly sophisticated, and now maintain internal information about the state of connections passing through them, the contents of some of the data streams, and so on. One thing that's an important distinction about many network layer firewalls is that they route traffic directly though them, so to use one you either need to have a validly assigned IP address block or to use a ``private internet'' address block [5]. Network layer firewalls tend to be very fast and tend to be very transparent to users.

In Figure 1, a network layer firewall called a ``screened host firewall'' is represented. In a screened host firewall, access to and from a single host is controlled by means of a router operating at a network layer. The single host is a bastion host; a highly-defended and secured strong-point that (hopefully) can resist attack.
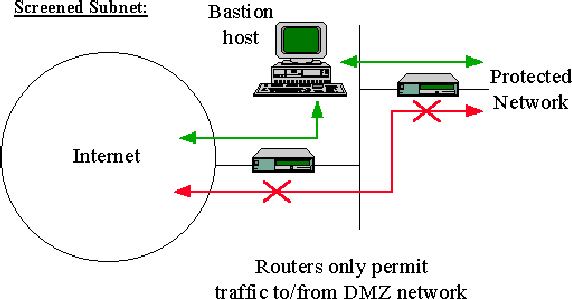
Example Network layer firewall: In Figure 2, a network layer firewall called a ``screened subnet firewall'' is represented. In a screened subnet firewall, access to and from a whole network is controlled by means of a router operating at a network layer. It is similar to a screened host, except that it is, effectively, a network of screened hosts.
(Continued on next question...)
Other Interview Questions
- Is Java secure?
- What are the risks?
- How common are security breaches?
- Who is at risk?
- How can I protect myself?
- What about products that claim to detect malicious applets?
- What about products that claim to block Java applets at a firewall?
- Which is more secure: Java or ActiveX?
- Which version of my browser should I use?
- What about ``hostile applets?''
- I run a Web server. Am I at risk?
- What about JavaScript?
- What’s the difference between code-based security and role-based security? Which one is better?
- How can you work with permissions from your .NET application?
- How can C# app request minimum permissions?
- What’s a code group?
- What’s the difference between authentication and authorization?
- What are the authentication modes in ASP.NET?
- Are the actual permissions for the application defined at run-time or compile-time?
- # What’s the difference between local, global and universal groups?
- # I am trying to create a new universal user group. Why can’t I?
- # What is LSDOU?
- # Why doesn’t LSDOU work under Windows NT?
- # Where are group policies stored?
- # What is GPT and GPC?
- # Where is GPT stored?
- # You change the group policies, and now the computer and user settings are in conflict. Which one has the highest priority?
- # You want to set up remote installation procedure, but do not want the user to gain access over it. What do you do? gponame–>
- # What’s contained in administrative template conf.adm?
- # How can you restrict running certain applications on a machine?
- # You need to automatically install an app, but MSI file is not available. What do you do?
- # What’s the difference between Software Installer and Windows Installer?
- # What can be restricted on Windows Server 2003 that wasn’t there in previous products?
- # How frequently is the client policy refreshed?
- # Where is secedit?
- # You want to create a new group policy but do not wish to inherit.
- # What is "tattooing" the Registry?
- # How do you fight tattooing in NT/2000 installations?
- # How do you fight tattooing in 2003 installations?
- # What does IntelliMirror do?
- # What’s the major difference between FAT and NTFS on a local machine?
- # How do FAT and NTFS differ in approach to user shares?
- # Explan the List Folder Contents permission on the folder in NTFS.
- # I have a file to which the user has access, but he has no folder permission to read it. Can he access it?
- # For a user in several groups, are Allow permissions restrictive or permissive?
- # For a user in several groups, are Deny permissions restrictive or permissive?
- # What hidden shares exist on Windows Server 2003 installation?
- # What’s the difference between standalone and fault-tolerant DFS (Distributed File System) installations?
- # We’re using the DFS fault-tolerant installation, but cannot access it from a Win98 box.
- # Where exactly do fault-tolerant DFS shares store information in Active Directory?
- # Can you use Start->Search with DFS shares?
- # What problems can you have with DFS installed?
- # I run Microsoft Cluster Server and cannot install fault-tolerant DFS.
- # Is Kerberos encryption symmetric or asymmetric?
- # How does Windows 2003 Server try to prevent a middle-man attack on encrypted line?
- # What hashing algorithms are used in Windows 2003 Server?
- # What third-party certificate exchange protocols are used by Windows 2003 Server?
- # What’s the number of permitted unsuccessful logons on Administrator account?
- # If hashing is one-way function and Windows Server uses hashing for storing passwords, how is it possible to attack the password lists, specifically the ones using NTLMv1?
- # What’s the difference between guest accounts in Server 2003 and other editions?
- # How many passwords by default are remembered when you check "Enforce Password History Remembered"?
- #1: Default protection from potentially dangerous Active X controls
- #2: Per-zone control of Active X opt-in
- #3: Site and zone locking for Active X controls
- #4: Protection against phishing
- #5: Cross-domain security
- #6: Locked down security zones
- #7: Better SSL/TLS notification and digital certificate info
- #8: Privacy protection features
- #9: Address bars
- #10: International character alert
- What is a network firewall?
- Why would I want a firewall?
- What can a firewall protect against?
- What can't a firewall protect against?
- What about viruses and other malware?
- Will IPSEC make firewalls obsolete?
- Where can I get more information on firewalls on the Internet?
- What are some of the basic design decisions in a firewall?
- What are the basic types of firewalls?
- Network layer firewalls
- Application layer firewalls
- What are proxy servers and how do they work?
- What are some cheap packet screening tools?
- What are some reasonable filtering rules for a kernel-based packet screen?
- What are some reasonable filtering rules for a Cisco?
- What are the critical resources in a firewall?
- What is a DMZ, and why do I want one?
- How might I increase the security and scalability of my DMZ?
- What is a `single point of failure', and how do I avoid having one?
- How can I block all of the bad stuff?
- How can I restrict web access so users can't view sites unrelated to work?
- What is source routed traffic and why is it a threat?
- What are ICMP redirects and redirect bombs?
- What about denial of service?
- What are some common attacks, and how can I protect my system against them?
- Do I really want to allow everything that my users ask for?
- How do I make Web/HTTP work through my firewall?
- How do I make SSL work through the firewall?
- How do I make DNS work with a firewall?
- How do I make FTP work through my firewall?
- How do I make Telnet work through my firewall?
- How do I make Finger and whois work through my firewall?
- How do I make gopher, archie, and other services work through my firewall?
- What are the issues about X11 through a firewall?
- How do I make RealAudio work through my firewall?
- How do I make my web server act as a front-end for a database that lives on my private network?
- But my database has an integrated web server, and I want to use that. Can't I just poke a hole in the firewall and tunnel that port?
- How Do I Make IP Multicast Work With My Firewall?
- What is a port?
- How do I know which application uses what port?
- What are LISTENING ports?
- How do I determine what service the port is for?
- What ports are safe to pass through a firewall?
- The behavior of FTP
- What software uses what FTP mode?
- Is my firewall trying to connect outside?
- The anatomy of a TCP connection
- Glossary of Firewall-Related Terms
|