Public Class HelloWorld
Public Class HelloWorld - This is the class declaration in VB.NET; the interesting thing
for VB developers is that VB.NET is a fully object-oriented language (so everything is a
Class here) . The class always ends with an "End Class".
`Public' - is the modifier to determine the scope of the class (for other modifiers refer
.NET framework SDK documentation or later parts of this tutorial). HelloWorld is the
class name given for the class. Consumers of the class will be accessing through this
name only
Public Shared Sub Main () - This is called as the entry point function because the
runtime after loading your applications searches for an entry point from which the actual
execution starts. C/C++ programmers will find this method very familiar (VB
Programmers remember Sub Main). All Applications (exe) must have a definition for the
Main Method. Try removing the Main method from your application and the compiler
will complain that "No Start Point Defined". This means that the Main Method is the
starting point of any application, in other words When you execute your Application
"Main" method is called first automatically.
'Public' - This is the Access modifier for the Method. Since the Main method should be
accessible to everyone in order for the .NET Runtime to be able to call it automatically it
is always defined as public.
'Shared' - indicates that the method is a Class Method. Hence it can be called without
making an instance of the class first.
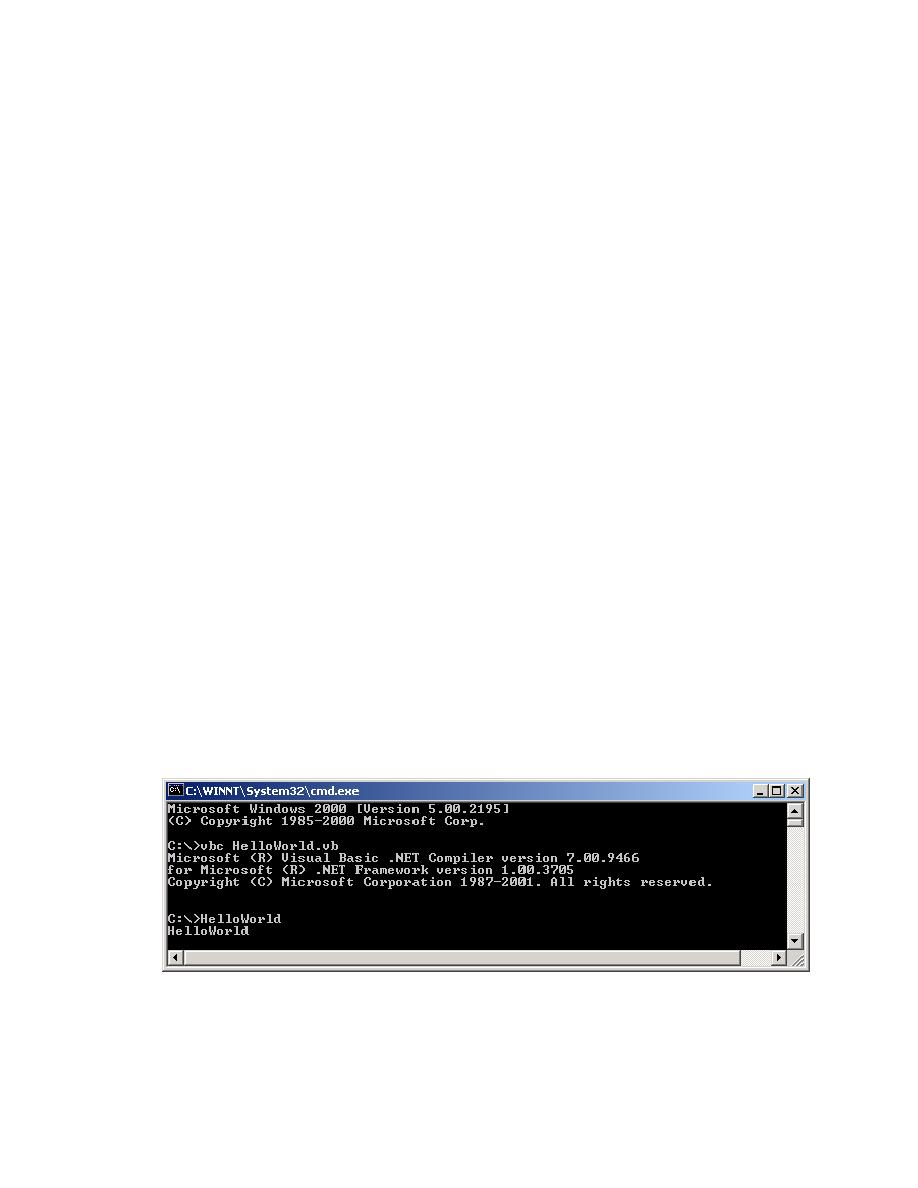
Now its time to compile and execute this complex program. To compile the above piece
of code you can use VB.NET compiler. To run the VB.NET compiler make sure you set
your path variable to point to the place where your VB.NET compiler is available. (To
set a new value in the path variable, go to control panel and double click System icon,
then choose advanced tab and click Environment Variables button to add or edit the
environmental variables)
Figure shows compilation of the HelloWorld program for VB.NET
file "HelloWorld.vb" compiles the same to produce a program that's not true executable,
instead it generates something called assembly. Here the VB.NET compiler produces a