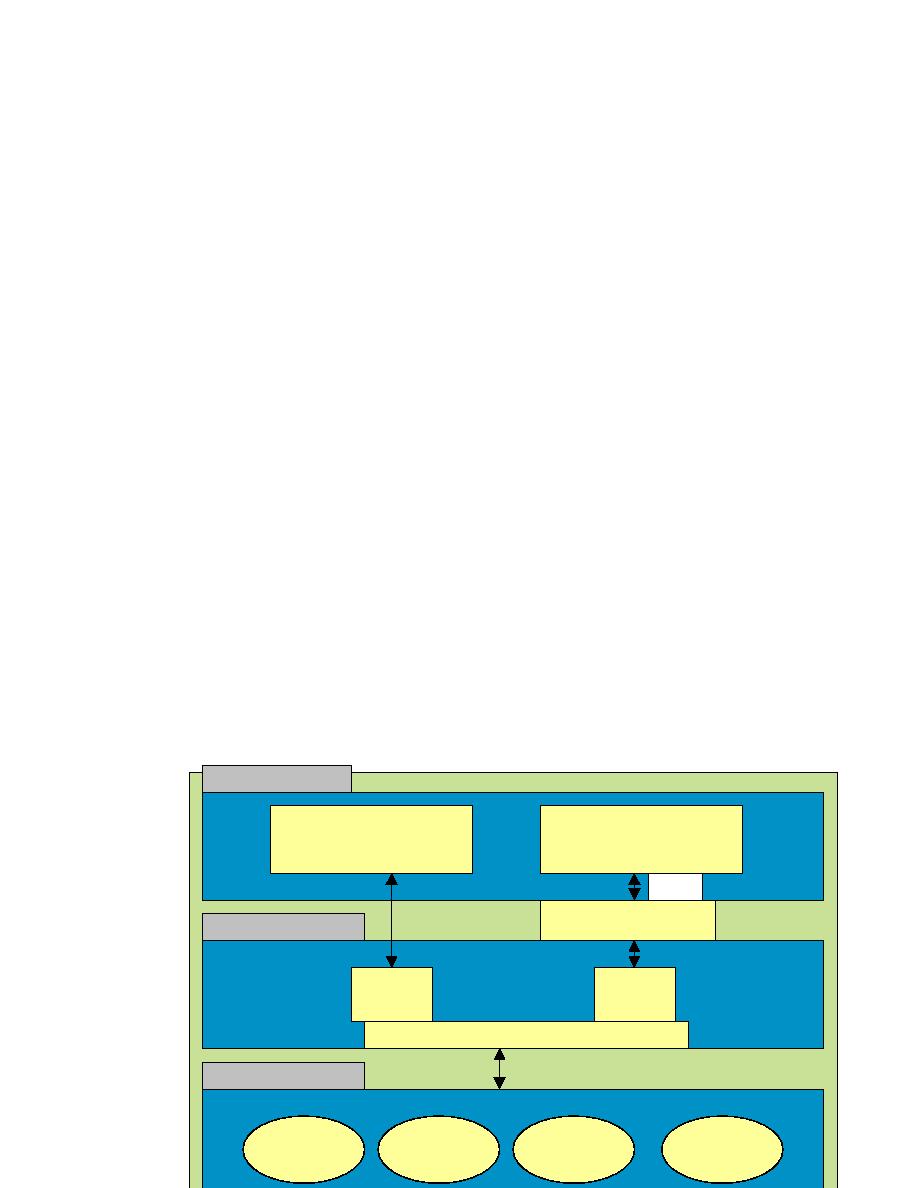
3-Tier Client Server Model
were soon not only being connected mutually but also to servers. Client/Server-
computing was born. A
from the user, interacting with the data services to perform the application's business
operations, and presenting the results of those operations to the user.
Things you might find in a presentation layer include a Web browser, a terminal, a
custom-designed GUI, or even a character-based user interface
applications and giving them a fancy windows-like front end, using PCs with terminal
emulators which presented pretty GUIs (Graphical user interface) or later Visual Basic
etc front-ends. A web browser talking to a web server is an example of a client talking to
a server. Here there is presentation logic (presentation tier) happening at the client, and
data/file access (data access tier) and logic happening at the server.
have been most commonly used since the 90's: Remote-SQL, ODBC, relatively
inexpensive and well-integrated PC-tools (like Visual Basic, Power-Builder, MS Access,
4-GL-Tools by the DBMS manufactures). In comparison the server side uses relatively
expensive tools. In addition the PC-based tools show good Rapid-Application-
Development (RAD) qualities i.e. simpler applications can be produced in a
comparatively short time. The 2-tier model is the logical consequence of the RAD-tools'
popularity.
html /xml
J
Applications
COM +
ASP